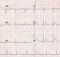
Waves in an Electrocardiogram
Waves in an Electrocardiogram
The usual waves in an ECG are P, QRS and T waves. P waves represent depolarization of the atria. QRS represents the depolarization of the ventricles. T wave is due to ventricular repolarization.
The repolarization wave of the atria is not usually visible on the surface electrocardiogram. If present, it is known as the Ta wave. The extent of Ta wave includes the PR segment, QRS and early part of the ST segment. Prominent Ta wave contributes to the upsloping ST depression sometimes seen during treadmill exercise test.
In addition to these certain waves occur in abnormal situations. A delta wave appears in pre-excitation while an epsilon wave appears in post excitation. Delta wave is a slurring of the initial portion of the QRS which resembles the Greek alphabet delta. Epsilon wave occurs at the end of the QRS and is seen in arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia.
An Osborn wave is visible at the end of the QRS in severe hypothermia. A normal variant known as J wave is also sometimes seen at the end of the QRS. A U wave may be seen after the T wave in certain cases, especially when there is bradycardia. U wave becomes more prominent in hypokalemia.