RHD MS jet on CW Doppler
RHD MS jet on CW Doppler
(See annotated image below)
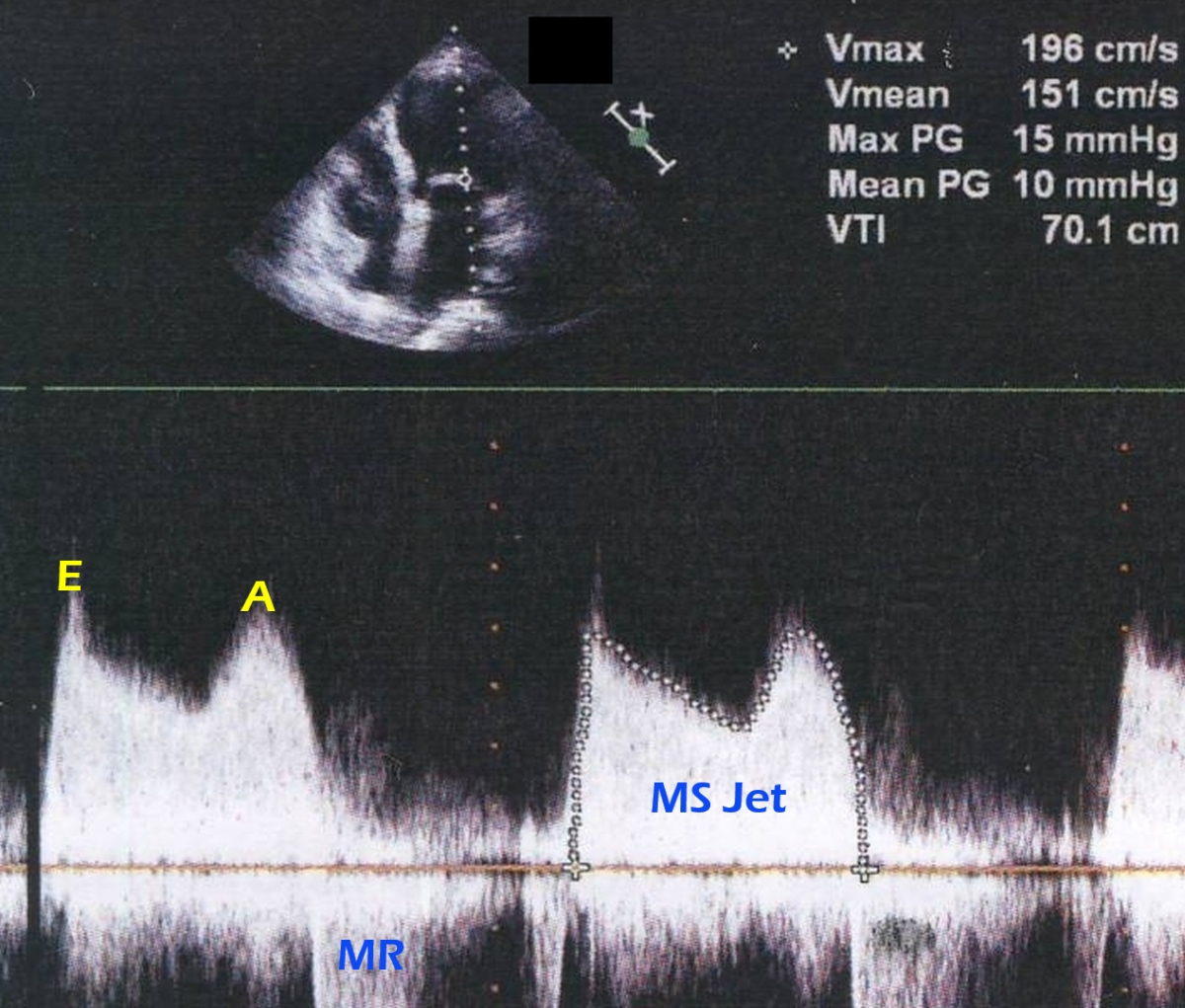
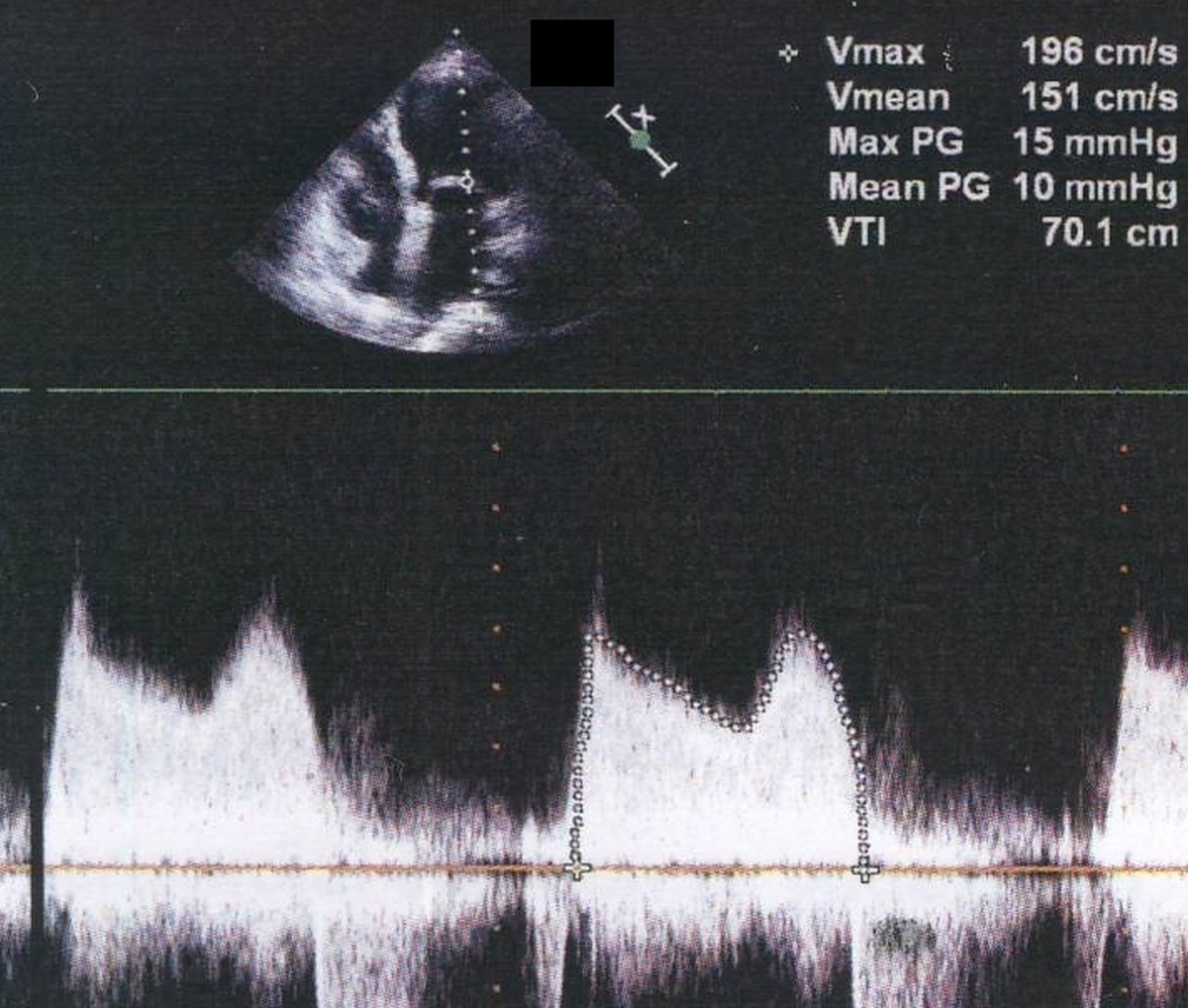
Continuous wave (CW) interrogation along the mitral valve in the apical four chamber view (upper channel) gives the M shaped Doppler pattern in mitral stenosis. The initial peak is early diastolic (E) while the later peak is atrial systolic (A). In a normal individual there will be a gap between these two waves due to the diastolic equalization of left atrial and left ventricular pressures (diastasis). Diastasis is absent in mitral stenosis because the gradient persists throughout diastole. The peak gradient (Max PG) is 15 mm Hg and the mean gradient (Mean PG) is 10 mm Hg. These correspond to a Vmax (maximal velocity) of 196 cm/second and a Vmean (mean velocity) of 151 cm/second. The velocity time integral (VTI) IS 70.1 cm. An incomplete jet seen below the baseline in systole is that of mild mitral regurgitation (MR). The slope of the E wave is used to determine the pressure half time from which the mitral valve area can be estimated. A pressure half time of 220 milliseconds will correspond to a valve area of 1 square centimeter. Hence 220 divided by the pressure half time will give the estimated mitral valve area in square centimeters.