M-mode echocardiogram in mitral stenosis
M-mode echocardiogram in mitral stenosis
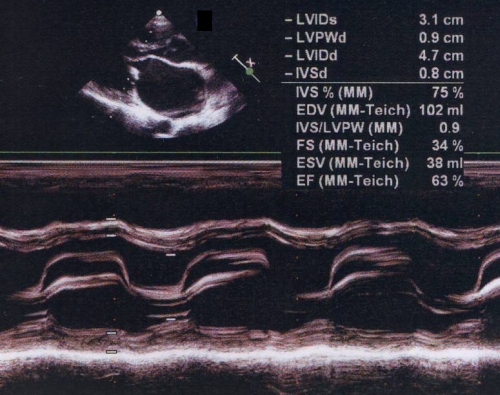
M-mode echocardiogram in mitral stenosis showing the flat EF slope and paradoxical motion of posterior mitral leaflet. Normally the anterior mitral leaflet shows and M shaped anterior movement and posterior mitral leaflet shows a smaller W shaped posterior movement pattern. The upper panel shows the doming of anterior mitral leaflet in diastole. The doming of the anterior mitral leaflet and the paradoxical anterior motion of the posterior mitral leaflet are the manifestations of commissural fusion seen in rheumatic mitral stenosis. The upper panel also shows a grossly dilated left atrium. LVIDs: left ventricular internal diameter, systolic; LVPWd: left ventricular posterior wall, diastolic; LVIDd: left ventricular internal diameter, diastolic; IVSd: interventricular septum, diastolic; EDV: end diastolic volume; FS: fractional shortening; ESV: end systolic volume; EF: ejection fraction. The difference between end diastolic and end systolic volume gives the stroke volume. Stroke volume divided by end diastolic volume gives the ejection fraction. Left ventricular ejection fraction is usually normal in mitral stenosis. IVS/LVPW ratio is abnormal in asymmetric septal hypertrophy of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. It can also be abnormal if the septum or the left ventricular posterior walls are thinned out due to myocardial infarction.