Conotruncal anomalies of the heart
Conotruncal anomalies of the heart
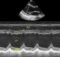
Conotruncal anomalies of the heart are the defects due to defective development of the outflow tracts of the ventricles. Tetralogy of Fallot, transposition of the great arteries, double outlet right ventricle and truncus arteriosus are the common types of conotruncal anomalies. Pulmonary atresia with ventricular septal defect and aortopulmonary window also form part of the spectrum of conotruncal anomalies. Genetic factors like trisomy 21, trisomy 13 and trisomy 18 are associated with conotruncal malformations. Chromosome 22q microdeletion is linked to DiGeorge syndrome and velocardiofacial syndrome. Fetal echocardiography can identify conotruncal anomalies in utero. Transposition of the great arteries, double outlet of the right ventricle and tetralogy of Fallot are commoner in males while truncus arteriosus is more common in females.